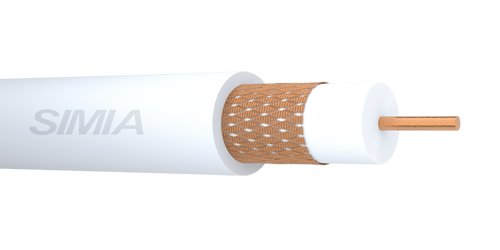
High Frequency Coaxial Cables
| Cable Type | No.& Nominal Diameter of Conductors (mm) | Nominal Diameter Over Insulation (mm) | Conductor Material | Impedance (Ω) | Attenuation at 100 MHz(dB) | Outer Diameter(mm) | Approx. Weight(Kg / Km) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.5C - 2V | 1x 0.4 | 2.4 | Copper | 75 | 52 | 4 | 23 |
| 3C - 2V | 1x 0.5 | 3 | Copper | 75 | 42 | 5.5 | 41 |
| 4.5C - 2V | 1x 0.9 | 4.5 | Copper | 75 | 22 | 6.5 | 47 |
| 5C - 2V | 1x 0.8 | 5 | Copper | 75 | 27 | 7.5 | 72 |
| 3C - 2W | 1x 0.5 | 3 | Copper | 75 | 42 | 6.5 | 68 |
| 5C - 2W | 1x 0.8 | 3 | Copper | 75 | 27 | 8.4 | 101 |
| RG - 6 | 1x 0.9 | 4.3 | Copper | 75 | 8.8 | 6.7 | 54 |
| RG - 8 | 7x 0.72 | 6.4 | Copper | 50 | 8 | 9.5 | 128 |
| RG - 11 | 7x 0.4 | 7.3 | Tinned Copper | 75 | 7.5 | 10.3 | 120 |
| RG - 58 | 19x 0.18 | 2.95 | Tinned Copper | 50 | 17 | 5 | 38 |
| RG - 59 | 1x 0.60 | 3.7 | Copper | 75 | 11.5 | 6.2 | 57 |
| RG - 213 | 7x 0.75 | 7.25 | Copper | 50 | 6.8 | 10.3 | 165 |
| RG - 214 | 7x 0.77 | 7.3 | Copper | 50 | 7.1 | 11 | 224 |
Technical Data
- High frequency coaxial cables, mostly used in H.F. transmissions.
Min. insulation resistance:
- 10,000MΩ.Km
Reference standard
- JIS C 3501
- MIL C 17
- IEC 60096
Temperature range
- - 30℃ to + 70℃
Cable Layer Construction
- Cu/PE/CWB/PVC
- Cu/FPE/CWB/PVC
- Cu/FPE/Al Foil/TCWB/PVC
- TiCu/PE/TCWB/PVC
- TiCu/FPE/TCWB/PVC
Cable Structure
- Conductor material: Plain or tinned copper conductor according to IEC 60228, class 1 (solid), class 2 (stranded) or class 5 (flexible).
- Insulation: Polyethylene, solid or foamed.
- Shield: Plain or tinned copper braid.
- Outer sheath: Compound type of PVC.
Application
These types of cables are used in high frequency transmissions specially for transmitters and receivers, computers, radio and TV transmissions.




بدون دیدگاه